How to audit affiliate links : a complete guide for marketers

You wake up to check your affiliate dashboard and notice something wrong.
Conversions have dropped by 40%. After investigation, you discover the problem : a broken redirect that has been killing your commissions for three days.
This scenario happens often. Affiliate links break, redirect chains change, and geo-targeting rules change, often without any warning from the merchant. The result? Lost revenue that you'll never recover.
Learning to audit affiliate links regularly is a critical skill in affiliate marketing. It protects your revenue, improves user experience, and keeps you compliant with requirements.
In this guide, you'll learn why auditing matters, how to do it manually, which tools can automate the process, and how to build a monitoring workflow that catches problems before they cost you money.
Why you need to audit affiliate links
Affiliate links are not static.
They exist within an ecosystem of tracking systems, redirect servers, and merchant platforms : all of which can change at any moment.
Common affiliate link problems
Several issues can break your affiliate links :
Broken redirects happen when merchants update their tracking systems, change affiliate platforms, or restructure their websites.
Your links might return 404 errors, redirect to homepage instead of product pages, or simply stop working entirely.

Geo-targeting issues are particularly sneaky. A link that works perfectly in the United States might redirect to a blocked page in Germany, or show a different content in Australia.
If you're promoting to international audiences, you could be losing conversions without knowing it.
Commission theft occurs when your affiliate parameters get stripped during redirects or when merchants accidentally break their tracking. Your clicks still generate sales, but you don't get credit.
Cloaking detection by affiliate networks can result in your links being blocked. If your cloaking plugin conflicts with the merchant's tracking or creates suspicious redirect patterns, you might get flagged.
Broken affiliate links = revenue leak
A single broken high-converting affiliate link can cost hundreds or thousands of dollars per month. If you're running campaigns across multiple posts and promotions, the potential losses multiply quickly.
If you have 50 affiliate links across your site, each generating an average of $100/month, and just 10% of them are broken or misdirecting traffic, you're losing $500 monthly. That's $6,000 per year from a problem you could catch in an hour of auditing.
Compliance and disclosure requirements
Beyond revenue, there's the legal angle. The FTC requires proper disclosure of affiliate relationships. If your affiliate links redirect through unexpected domains or don't clearly indicate their affiliate nature, you could face compliance issues.
Regular audits help you verify that your disclosures remain accurate and that your links behave as expected from a regulatory standpoint.
Manual methods to audit affiliate links
Understanding manual auditing methods helps you appreciate what automated solutions handle for you. These techniques also remain useful for spot-checking specific links.
Click-through testing
The most basic method is simply clicking your links and following the redirect chain. Open each affiliate link, observe where it takes you, and verify you land on the expected page with your affiliate parameters intact.
This works for small sites with few links, but becomes impractical once you have hundreds or thousands of affiliate links to monitor.
Using browser developer tools
For deeper inspection, browser developer tools reveal what happens during redirects. In Chrome, open DevTools (F12), go to the Network tab, and check "Preserve log" before clicking your affiliate link.
You'll see every request in the redirect chain, including HTTP status codes, response headers, and the final destination URL. Look for 301/302 redirects, any unexpected domains in the chain, and whether your affiliate ID appears in the final URL.
Alternatively, you can use a chrome extension like Redirect Path to analyze the path.
Testing from different locations
Geo-targeting issues require testing from multiple locations. VPN services let you simulate clicks from different countries, but this approach has limitations.
Free VPNs often use flagged IP addresses that merchants block. Even premium VPNs might not represent real user behavior in target markets. You'll also need to remember to test from each relevant country manually.
Spreadsheet tracking
Many affiliate marketers maintain spreadsheets listing every affiliate link on their site. Columns might include the link URL, expected destination, affiliate network, last tested date, and current status.
This organizational approach helps, but requires discipline to maintain. It also doesn't solve the actual testing problem, you still need to check each link manually.
Limitations of manual auditing
Manual methods share common weaknesses. They're time-consuming, making regular audits impractical. They don't scale as your site grows. They can't detect intermittent issues that occur only at certain times or from certain locations. And they rely on you remembering to perform checks regularly.
For sites with more than a handful of affiliate links, automated solutions become necessary.
Automated tools to audit affiliate links
Several tools can automate the affiliate link audit process. Each has different strengths depending on your needs.
Option 1: Screaming Frog SEO Spider
Screaming Frog is primarily an SEO crawler, but it can help with affiliate link auditing by crawling your site and extracting all outbound links.
How to use it for affiliate auditing:
Start by crawling your website with Screaming Frog. Once complete, filter for external links and export them. You can then identify which are affiliate links based on their domains or URL patterns.
The tool shows HTTP status codes for each link, helping you identify 404 errors or server issues. You can also see redirect chains by configuring the crawler to follow redirects.
Pros:
Screaming Frog excels at comprehensive site-wide link extraction. It works locally on your machine, handles large sites efficiently, and integrates well into SEO workflows.
Cons:
The tool has important limitations for affiliate link auditing. Many affiliate networks and merchants block crawlers, returning 403 Forbidden status codes even for working links. You can't test geo-targeting since it crawls only from your location. And it doesn't support continuous monitoring, each audit requiring a new crawl.
Best for: One-time audits to extract all affiliate links from your site. Use it to build your initial inventory, then test the links with other tools.
Option 2: PageRadar Affiliate Link Checker
PageRadar's Affiliate Link Checker is designed specifically for affiliate marketers who need to monitor links across multiple countries.
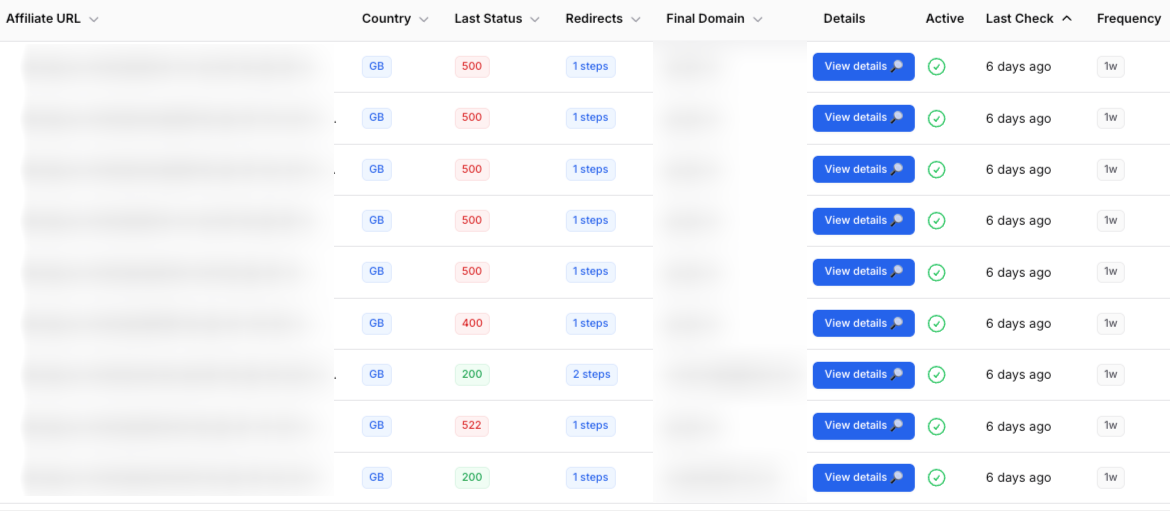
Key features:
The tool tests affiliate links from 167 countries using residential proxies. This means you see exactly what real users in each target market experience, including geo-blocks, regional redirects, and country-specific restrictions.
It traces complete redirect chains up to 10 hops, showing you every intermediate step between your link and the final destination. You can detect when merchants change their tracking systems or when unexpected redirects appear.
For ongoing protection, paid plans include continuous monitoring with email alerts. When a link breaks, redirects change, or geo-blocks appear, you receive immediate notification with full context about what changed.
Pros:
Purpose-built for affiliate link monitoring. Geo-targeting detection from 167 countries. Real residential proxies that behave like actual users. Continuous monitoring options. Free tool available for testing individual links.
Cons:
Requires manually adding links for monitoring rather than discovering them automatically. Best used in combination with a crawler like Screaming Frog for initial link extraction.
Best for: Regular monitoring of high-value affiliate links. Testing geo-targeted campaigns. Detecting issues before they impact commissions.
Option 3: Generic link checkers
Tools like Dead Link Checker, Broken Link Check, and similar services can identify broken links on your site. They're simple to use : enter your URL, and they crawl for dead links.
However, these tools have significant limitations for affiliate link auditing. They typically can't follow complex redirect chains. They don't detect geo-targeting issues. They treat 301 redirects as "working" even when the final destination is wrong. And they don't distinguish affiliate links from regular links.
When to use them: These tools work for basic broken link detection across your entire site. They're free and fast. But they shouldn't be your only auditing method for affiliate links.
Step-by-step: how to audit affiliate links
Here's a practical workflow combining the strengths of different tools.
Step 1: list all affiliate links on your site
Use Screaming Frog to crawl your website and extract all outbound links.
Filter for affiliate links. Common patterns include Amazon affiliate links (containing tag= parameter), network links (shareasale.com, cj.com, etc.), and any cloaked links from plugins like ThirstyAffiliates or Pretty Links (/go, /ir, etc...).
Create a spreadsheet with columns for: Link URL, Source Page, Affiliate Network, Product/Offer, and Priority (based on traffic or commission value).
Step 2: Test each link's redirect chain
For each affiliate link, verify the complete redirect path. With PageRadar's free tool, enter your link and select your primary target country. The tool shows every redirect step from your link to the final destination.
Check that the final URL matches expectations. Verify your affiliate ID appears in the destination URL. Note any unusual intermediate domains or unexpected redirects.
Step 3: Verify geo-targeting
If you target international audiences, test your links from each relevant country. Some affiliate programs show different offers or block certain regions entirely.
Using PageRadar, test the same link from different countries. Compare the final destinations. Document any geo-specific behavior so you can adjust your strategy accordingly, perhaps using different affiliate programs for different regions.
Step 4: Check final destination URLs match expectations
Beyond just "working," verify that links land where they should. A link to a specific product should reach that product page, not the homepage. A link to a sale page should still show the sale.
Common issues include: products going out of stock (link redirects to category page), merchants restructuring sites (old URLs redirect to new locations), and seasonal promotions ending (sale pages become regular pages).
Step 5: Monitor commission tracking
While you can't directly verify commission tracking through link checking, you can look for warning signs. Missing or changed affiliate parameters in final URLs. Unexpected domains in redirect chains that might strip tracking. Discrepancies between your click counts and affiliate dashboard reports.
If you suspect tracking issues, contact your affiliate manager with specific evidence from your redirect chain analysis.
Step 6: Document and schedule regular re-audits
Create a recurring calendar event for affiliate link audits. Monthly works well for most sites. Weekly makes sense for high-volume affiliate marketers or during promotional periods.
For critical links, those generating significant revenue, set up continuous monitoring through a tool like PageRadar. You'll receive alerts when issues occur rather than discovering them during audits.
Best practices for affiliate link management
Building good habits around affiliate link management prevents problems before they occur.
Establish regular audit schedules
Choose an audit frequency based on your site's size and revenue. Minimum: quarterly comprehensive audits. Recommended: monthly quick checks. Optimal: continuous monitoring for high-value links with quarterly deep audits for everything else.
Mark these audits in your calendar as non-negotiable. Treat them like any other business-critical task.
Maintain documentation and tracking systems
Keep records of every affiliate link on your site. Include the link URL, expected destination, affiliate network, commission rate, date added, and last verified date.
This documentation serves multiple purposes. It speeds up audits since you know what to check. It helps identify patterns when issues occur. It supports compliance by tracking what disclosures apply where.
Set up alerts for broken links
Don't rely solely on periodic audits. Use monitoring tools that notify you when problems occur. A link that breaks today might not be caught until next month's audit without automated monitoring.
Configure alerts to reach you quickly : mail works for most cases, but consider Slack or SMS for your highest-value links.
Test before and after site updates
Any time you update your website (new theme, plugin updates, URL restructuring) test your affiliate links afterward. These updates can inadvertently break link cloaking, modify redirect behavior, or remove affiliate parameters.
Build affiliate link testing into your deployment checklist. A five-minute check after updates can prevent days of lost commissions.
